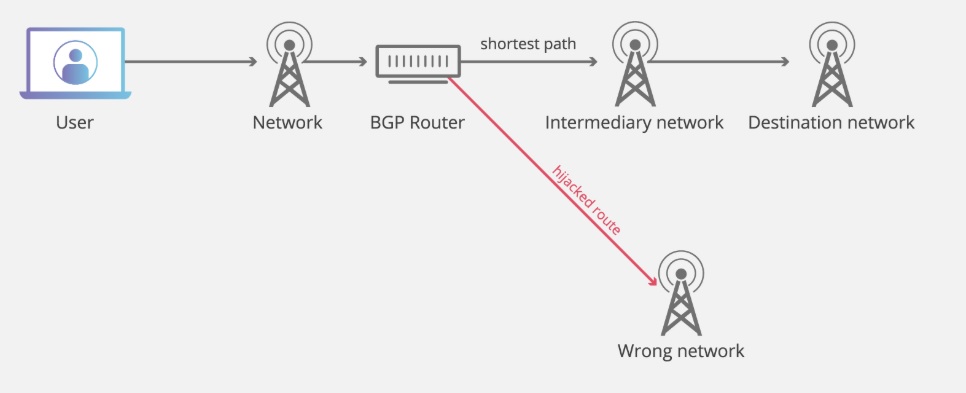
BGP Hijacking is a kind of cyberattack; the Internet traffics are rerouted to the attacker’s server or dead-end instead of a legitimate destination. BGP is the most important and underlying protocol on which the internet routing works. Due to BGP hijacking, the data packets rerouted and are intercepted by attackers leads to the MITM attack, i.e., Man in the middle attack.
What is BGP?
BGP stands for Border gateway protocol. BGP makes data transmission possible between different AS’s(autonomous systems) or networks. In short, we can say it provides the direction and shortest path for faster data transmission on the Internet. Any network that is connected to the Internet relies on BGP to reach out to other systems. And by definition, the Internet is the most extensive interconnected network, and routing protocol like BGP makes the Internet even faster.
BGP router stores the routing information in the routing tables with the best and shortest routes between AS’s. Whenever an Internet service provider (ISP) broadcasts new Internet protocol (IP) prefixes they own, the routing table is continually updated. The underlying principle behind BGP is that it follows the shortest and most direct path between AS to AS, by making sure the data packets are crossing the fewest possible hops.
Must Read : Why is Cloud Security Important?
How is BGP Hijacking possible?
As we know, there is no governing body present in the world of the Internet; it makes it difficult to monitor and govern the traffic. Above all, BGP works on the assumption that interconnected autonomous systems are telling the truth regarding owning the IP address, which gives attackers the scope to exploit. Thus, the Border Gateway Protocol hijacking is nearly impossible to stop.
What are the signs of BGP Hijacking?
- The page loading time increases drastically because network requests are no longer following the most efficient route and possibly traversing around different servers unnecessarily.
- The total network traffic is redirected to a dead-end, i.e., intentionally restricting users from accessing the Internet and sometimes forcing them to change the ISP.
- Specific websites are unreachable and preferably redirected to fake sites for stealing user credentials, opening the door to more significant fraud.
- BGP hijackings may also be used as part of a disinformation campaign or as part of complicated phishing attacks.
BJP Hijacking in Real-world :
- A case has been reported for Russian state-owned telecommunications provider, Rostelecom. The hijack redirected more than 8800 major internet traffic routes through its server.
- In April 2018, a Russian Internet Service Provider, announced several IP prefixes (groups of IP addresses) that belong to Amazon DNS servers Route53. In short, the result was that users attempting to log in to a cryptocurrency site were getting redirected to a fake variant of the website controlled by hackers. The hackers were thus able to steal almost $152,000 in cryptocurrency.
- In 2008, the Pakistani government-owned Pakistan Telecom attempted to censor YouTube within Pakistan by updating its BGP routes for the website. Accidentally, the new routes were announced to Pakistan Telecom’s upstream providers, and from there, broadcast to the whole Internet. Suddenly, all web requests for YouTube were directed to the Pakistan Telecom website, resulting in an hour-long outage of the site for almost the entire Internet, and overwhelming the ISP.
Interesting Read: Does Taping your Webcam Provide Cyber Security? A Myth Debunked
How to prevent BGP hijacking?
- Mutually Agreed Norms for Routing Security (MANRS) is a community initiative of network operators and Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) that establishes a baseline of routing security expectations.
- Network providers should monitor their network traffic constantly with industry grade network monitoring tools like BGPmon.
- A system like Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) and Prefix filtering can significantly reduce the chance of BGP hijacking, making the over communication faster and secure.
- Replace BGP with Border Gateway Protocol Security (BGPSec) is a security extension of the Border Gateway Protocol. The protocol needs to be implemented throughout the globe, which is difficult considering the requirement and choices of the individual network.
Conclusion:
Even though it’s hard to stop BGP hijacking attacks on the Internet, Internet Service Providers and Autonomous Systems can always adopt extra security measures to prevent. The immediate action includes monitoring their networks, prefix filtering, and many more to make the global network more secure.

Leave a Reply